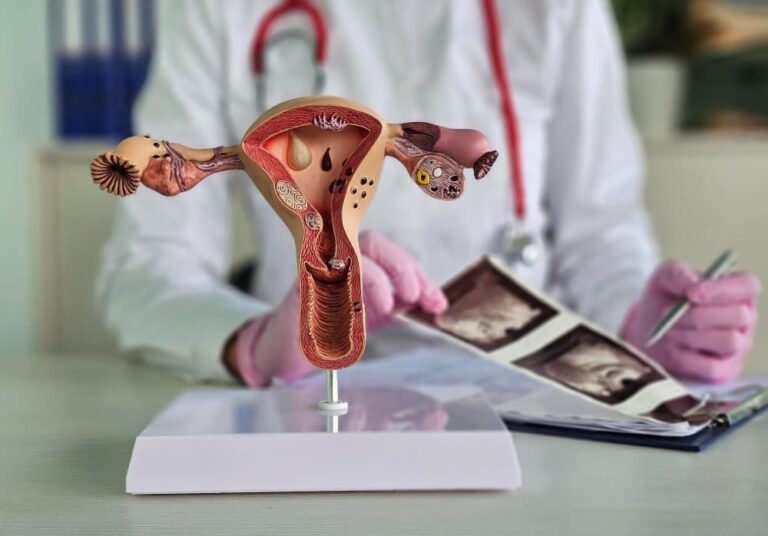
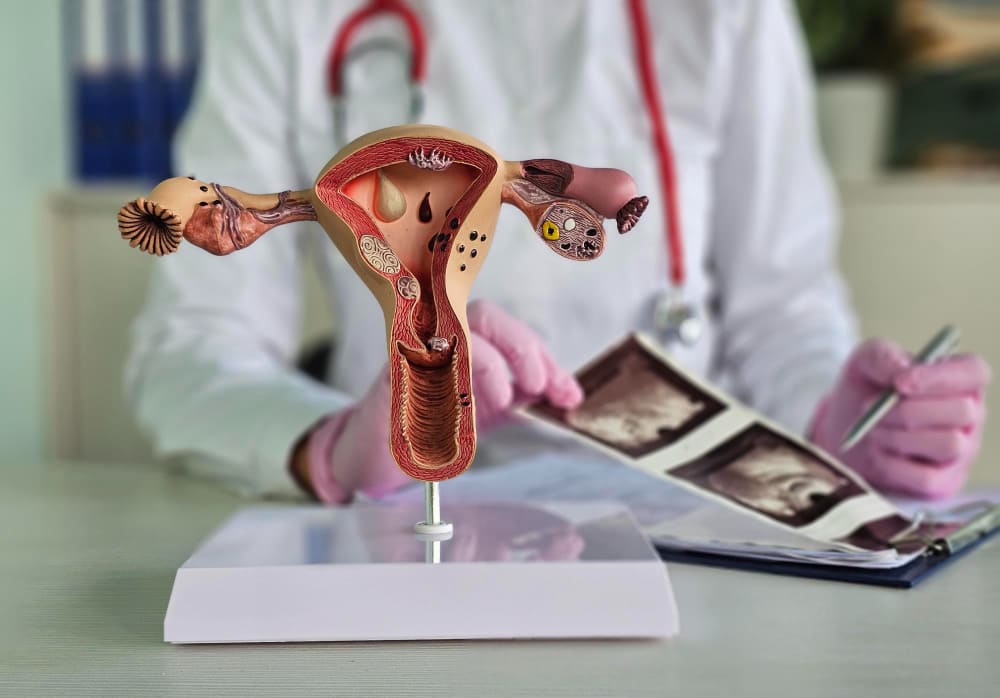
Adenomyosis symptoms include heavy menstrual bleeding, severe cramping, and pelvic pain. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment of this often-misdiagnosed condition.
Understanding Adenomyosis Symptoms
Adenomyosis is when the endometrial tissue, which normally lines the uterus, abnormally grows into the uterine muscle (myometrium). This can cause a range of symptoms, often mistaken for other gynecologic conditions like endometriosis or fibroids. Let’s explore the common symptoms that characterize this condition and how they impact the lives of those affected.
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Menorrhagia) 🩸
One of the hallmark symptoms of adenomyosis is heavy menstrual bleeding. Women with this condition often experience prolonged periods, with blood loss so severe that it can lead to anemia. Large blood clots are also familiar, making each menstrual cycle particularly challenging and disruptive.
Severe Menstrual Cramps (Dysmenorrhea)
Adenomyosis is notorious for causing severe cramping during menstruation. The cramping can be sharp and intense, often described as “knife-like” pain. This discomfort isn’t limited to the lower abdomen but can radiate to the pelvis, lower back, and even the thighs. Many women report that these cramps worsen over time, making each cycle more unbearable than the last.
Pelvic Pain and Pressure
Chronic pelvic pain is another common symptom of adenomyosis. This pain can be constant or intermittent and is often accompanied by a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the lower abdomen. The uterus may become enlarged due to the diffusely growing endometrial tissue, which exacerbates the discomfort and can cause a feeling of fullness or bloating.
Painful Intercourse (Dyspareunia)
Pain during or after sex is a distressing symptom that many women with adenomyosis experience. The deep, sharp pain during intercourse is often due to the inflamed and thickened uterine walls. This symptom can significantly impact relationships and sexual well-being.
Irregular Periods and Menstrual Abnormalities
Adenomyosis can cause irregular menstrual cycles, with periods that are more frequent, last longer or are unusually heavy. Some women may also experience spotting between periods, which adds to the unpredictability and frustration of managing this condition.
Abdominal and Pelvic Discomfort
Beyond the intense menstrual cramps, many women with adenomyosis report a constant, dull ache in the lower abdomen and pelvis. This discomfort can extend to the rectum and bladder, increasing urinary frequency and bowel issues. The pain and pressure can be so severe that it interferes with daily activities and reduces the quality of life.
Bloating and Abdominal Fullness
Bloating and a persistent feeling of fullness in the abdomen are common in women with adenomyosis. This is often due to the enlarged uterus pressing against other organs, causing discomfort and a visible distension of the stomach.
Fertility Issues
Adenomyosis is sometimes linked to fertility problems. The abnormal growth of endometrial tissue within the uterine wall can impair the implantation of an embryo, leading to difficulties in conception or an increased risk of miscarriage.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing adenomyosis can be challenging, as its symptoms overlap with those of other conditions like endometriosis and fibroids. However, through careful evaluation, including physical exams, imaging (like ultrasound or MRI), and a thorough medical history, healthcare providers can often identify the presence of adenomyosis.
Once diagnosed, treatment options vary based on the severity of symptoms and the patient’s desire to preserve fertility. Treatments may range from pain management with NSAIDs to hormonal therapies that help reduce menstrual bleeding and pain. In more severe cases, surgical options like uterine artery embolization or even hysterectomy may be considered.
Best Treatment Options for Adenomyosis
The best treatment options for adenomyosis vary depending on the severity and specific symptoms. Uterine catheterization (uterine artery embolization) is highly effective, particularly in reducing heavy menstrual bleeding and severe pain.
Hormonal therapies, including GnRH agonists and progestin IUDs, help regulate menstrual cycles and alleviate symptoms by targeting the endometrial tissue that abnormally grows within the uterine wall.
For those with mild symptoms, NSAIDs can manage discomfort and cramping. In cases where fertility preservation is not a concern, a hysterectomy provides a permanent solution by removing the affected uterus. Physical examination and imaging are essential for accurate diagnosis and determining the most suitable treatment plan.
Living with Adenomyosis 🌼
While adenomyosis can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life, understanding the symptoms and seeking early treatment can help manage the condition. Regular consultations with a healthcare provider, along with a personalized treatment plan, can alleviate the painful and disruptive symptoms, allowing women to regain control over their lives.
For those struggling with adenomyosis, it’s essential to learn about the condition, share experiences with others, and seek support from healthcare professionals. With the right approach, the symptoms of adenomyosis can be managed effectively, leading to a more comfortable and fulfilling life.
☑️ How I cured my adenomyosis without surgery?
FAQS
Can adenomyosis heal itself?
Adenomyosis does not typically heal itself. Symptoms may improve after menopause when estrogen levels drop, but the condition usually requires medical management to alleviate symptoms.
What causes adenomyosis to flare up?
Adenomyosis symptoms can flare up due to hormonal fluctuations, particularly increased estrogen levels, which can lead to more severe pain and heavier bleeding during menstrual cycles.
What not to do with adenomyosis?
Avoid ignoring symptoms or delaying treatment, as this can lead to worsening pain and complications. Strenuous physical activities that exacerbate pelvic pain should also be minimized. Consulting a healthcare provider to create an appropriate management plan is essential.
What is the best treatment for adenomyosis?
The best treatment for adenomyosis can be uterine catheterization, also known as uterine artery embolization (UAE). This minimally invasive procedure effectively reduces symptoms by cutting off the blood supply to the affected areas of the uterus, causing the adenomyosis tissue to shrink.
☑️ Understanding Adenomyosis: When the Uterine Lining Grows into the Muscle